Search This Blog
Most Popular
Solar Paint: Converting Building Surfaces into Solar Power
March 26, 2025
Categories
- Building Construction (82)
- Building Materials (81)
- Columns (2)
- Concrete Beam (3)
- Concrete Construction Techniques (4)
- Concrete Mix Design (10)
- Concrete Repair (14)
- Concrete Slab (10)
- Construction Equipment (16)
- Construction News (7)
- Design of Structures (15)
- Engineering Drawing (1)
- Estimation (3)
- Geotechnical engineering (26)
- Highway Engineering (11)
- Innovations (29)
- Material Testing (9)
- Matrix Analysis of Structures (2)
- Mechanical Engineering (3)
- Strength of Materials (2)
- Structural Analysis (17)
- Structural Design (21)
- Structures (17)
- Transportation Engineering (9)
Concrete for Prevention of Air Pollution -Photocatalytic Concrete
Neenu
June 08, 2023
Concrete, the most widely consumed building material globally, has long been associated with significant carbon emissions, contributing around 8 percent of global greenhouse gases. It is also a major contributor to local air pollution. However, there is a new development that aims to address these environmental concerns by designing concrete for the prevention of air pollution.
Introducing photocatalytic concrete, a newly demonstrated material that exhibits air-scrubbing properties, effectively reducing air pollution in its vicinity. With traffic being a prominent source of air pollution, these innovative air-purifying concrete systems offer a promising solution until greener vehicle alternatives become more prevalent.
Photocatalytic concrete is known by different names like particle-eating concrete, self-cleaning concrete, or as a type of smog-eating product.
Let’s dive into the core concept behind photocatalytic concrete and its latest advancements as an air-purifying construction material.
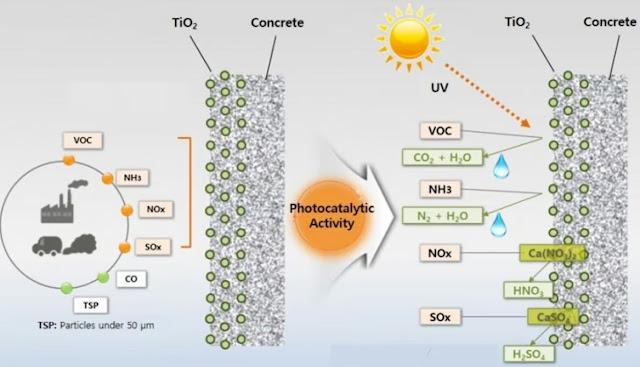
The photocatalytic reaction occurs when the light energy is higher that the photocatalyst band gap. After the reaction, the decomposed pollutants are taken away by the wind, water, or rain, achieving the function of air depollution and self-cleaning.
Photocatalytic concrete has the capability to perform air depollution, self-cleaning, and self-disinfecting. It can breakdown the air pollutants like volatile organic compounds (VOCs), sulfur oxides, nitrogen oxides, and ammonia thereby preventing the formation of fine particulate matter.
The below diagram illustrates how the new air-purifying concrete works. A layer of titanium dioxide interacts with sunlight (or artificial light) to produce reactive oxygen species, which degrade air pollutants like nitrogen oxides, sulfur oxides, volatile organic compounds, and ammonia into harmless end products.Let’s dive into the core concept behind photocatalytic concrete and its latest advancements as an air-purifying construction material.
What is Photocatalytic Concrete?
Photocatalytic concrete or self-cleaning concrete is an environmentally friendly concrete material that breaks down dirt, mold, and pollution in the environment by the photocatalytic reaction. This concrete system consists of a coating of titanium oxide which reacts with the sunlight to produce molecules called reactive oxygen species (ROS) that is the main hero behind breaking down the air pollutants.The photocatalytic reaction occurs when the light energy is higher that the photocatalyst band gap. After the reaction, the decomposed pollutants are taken away by the wind, water, or rain, achieving the function of air depollution and self-cleaning.
Photocatalytic concrete has the capability to perform air depollution, self-cleaning, and self-disinfecting. It can breakdown the air pollutants like volatile organic compounds (VOCs), sulfur oxides, nitrogen oxides, and ammonia thereby preventing the formation of fine particulate matter.
Photocatalytic Concrete for Traffic Tunnels
A new study conducted at the Korea Institute of Civil Engineering and Building Technology (KICT) developed photocatalytic concrete and applied it on a traffic tunnel, where the air pollution rate was comparatively high. To activate the photocatalytic reaction, artificial lights were installed as shown in the figure below.| Image Credits: Korea Institute of Civil Engineering and Building Technology |
Real Examples of Photocatalytic Concrete
Photocatalytic concrete has been successfully implemented in various real-world scenarios. For instance, the "Palazzo Italia" pavilion at the 2015 Milan Expo utilized photocatalytic concrete panels to actively reduce air pollution in its vicinity. In Mexico City, the "Smog Eating Building" transformed its facade using photocatalytic concrete, contributing to improved air quality.
 |
| Jubilee Church in Rome |
Another noteworthy application can be seen in the new Jubilee Church in Rome, where a photocatalytic additive in the concrete ensures that its brilliant white appearance remains clean and vibrant for years. These examples showcase how photocatalytic concrete can be used to tackle air pollution, enhance sustainability, and maintain the aesthetic appeal of architectural structures.
Potential Applications of Photocatalytic Concrete
Urban Areas
Photocatalytic concrete can be used in various urban areas where air pollution is a significant concern, such as busy streets, pedestrian walkways, and public squares. Incorporating this innovative material into sidewalks, pavements, and buildings, has the potential to actively reduce air pollution levels and improve the overall air quality in densely populated areas.
Transportation Infrastructure
Highways, bridges, and tunnels are major sources of air pollution due to vehicle emissions. Implementing photocatalytic concrete in these structures can help mitigate pollution by breaking down pollutants emitted from vehicles passing through. This application can be particularly effective in reducing pollution hotspots and improving the air quality around transportation corridors.
Industrial Zones
Industrial areas often face air pollution challenges due to emissions from manufacturing processes. Photocatalytic concrete can be employed in these zones to minimize the impact of industrial pollutants and create cleaner working environments for employees. By incorporating this concrete into the construction of industrial buildings and facilities, it can actively contribute to reducing local air pollution.
Benefits of Photocatalytic Concrete
Air Pollution Reduction
The primary advantage of photocatalytic concrete is its ability to reduce air pollution levels by breaking down harmful pollutants. By degrading nitrogen oxides, sulfur oxides, volatile organic compounds, and ammonia into harmless substances, it promotes air depollution and contributes to improved air quality.
Self-Cleaning Properties
Photocatalytic concrete's self-cleaning abilities are another notable benefit. As it breaks down dirt, mold, and organic matter, the concrete surface remains cleaner and requires less maintenance compared to traditional concrete. This feature enhances the aesthetic appearance and durability of structures while reducing cleaning costs.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Utilizing photocatalytic concrete can help reduce the environmental impact of construction. By actively reducing air pollution and its associated health risks, this material aligns with sustainability goals and contributes to a healthier and greener built environment.
Limitations and Considerations
Light Dependency
The efficiency of photocatalytic concrete depends on the availability of light. In areas with limited sunlight or insufficient artificial lighting, the air purification and self-cleaning properties may be less effective. Therefore, the location and appropriate lighting infrastructure should be considered when implementing this concrete.
Maintenance and Durability
While photocatalytic concrete can withstand weathering and maintain its air-purifying properties over time, regular maintenance is still necessary to ensure optimal performance. Routine inspections and cleaning may be required to remove debris or substances that could hinder the photocatalytic reaction.
Cost Considerations
Photocatalytic concrete may initially involve higher costs compared to traditional concrete due to the additional manufacturing processes and the use of titanium dioxide coatings. However, the long-term benefits, such as improved air quality and reduced maintenance costs, should be evaluated to assess the overall economic viability.
In conclusion, photocatalytic concrete presents an innovative solution for addressing air pollution concerns in various applications. Its potential to actively reduce air pollutants, self-clean, and contribute to sustainable building practices makes it a promising material for creating cleaner and healthier urban environments. Careful consideration of its limitations and cost implications is necessary when implementing this technology to maximize its effectiveness and benefits.
In conclusion, photocatalytic concrete presents an innovative solution for addressing air pollution concerns in various applications. Its potential to actively reduce air pollutants, self-clean, and contribute to sustainable building practices makes it a promising material for creating cleaner and healthier urban environments. Careful consideration of its limitations and cost implications is necessary when implementing this technology to maximize its effectiveness and benefits.
Also Read: Self-Healing Concrete
Most Visited
Sieve Analysis of Aggregates - ASTM Standard
August 11, 2021
How to Calculate Cement Required for Floor Tiling?
July 02, 2020
What are Infiltration Wells?
April 15, 2024
Cross-Section of a Road – Geometric Design of Highways
February 26, 2021
How to Choose Good Quality Aggregates for Construction?
August 10, 2021
Traverse Surveying - Objective, Method and Procedure
January 19, 2022
Construction ERP System – A Comprehensive Guide
December 12, 2024
Top 7 Waterproofing Materials for Concrete Roofs
December 13, 2024
Search This Blog
MUST READ
What is PERT? Objectives, Pros & Cons
September 10, 2017
Terzaghi's Equation: Soil Bearing Capacity for Foundations
March 02, 2022
Contact Form
Footer Menu Widget
Created By SoraTemplates | Distributed By Gooyaabi Templates


0 Comments
Commenting Spam Links Are Against Policies