Search This Blog
Most Popular
Categories
- Building Construction (84)
- Building Materials (82)
- Columns (2)
- Concrete Beam (3)
- Concrete Construction Techniques (4)
- Concrete Mix Design (9)
- Concrete Repair (14)
- Concrete Slab (10)
- Construction Equipment (16)
- Construction News (7)
- Design of Structures (15)
- Engineering Drawing (1)
- Estimation (3)
- Geotechnical engineering (26)
- Highway Engineering (11)
- Innovations (30)
- Material Testing (10)
- Matrix Analysis of Structures (2)
- Mechanical Engineering (3)
- Strength of Materials (2)
- Structural Analysis (17)
- Structural Design (21)
- Structures (17)
- Transportation Engineering (9)
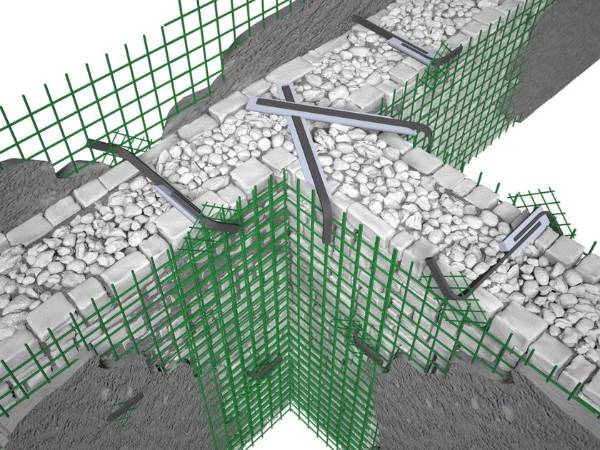
Mesh Reinforcement for Concrete Structures
Mesh reinforcement is a type of reinforcement in the form of a series of interconnected wires or bars arranged in a grid pattern. These meshes are used to reinforce and strengthen concrete structures like slabs, foundations, retaining walls, etc.
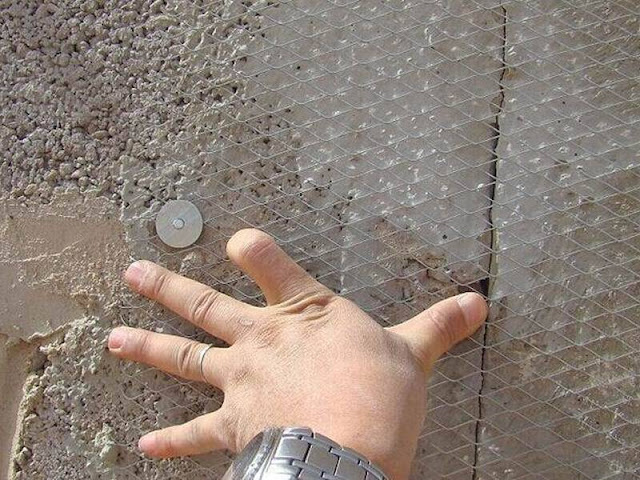 |
| Image Credits: Walcoom |
It's true, steel reinforcement is superior to mesh reinforcement in different ways. But there are situations where you really require mesh over rebars for your construction project, which not only saves time but also your money.
This article outlines the different grades and features of mesh reinforcement for construction, along with situations you should employ mesh over steel rebars.
History of Mesh Reinforcement
The mesh reinforcement system was derived back in the 20th century by German Engineer Eugen Schumann. The developed mesh consists of steel wires made from low-carbon steel woven together to create a mesh. This mesh system was inexpensive and easy to work with, which then became a popular way to reinforce concrete.
However, this reinforcement option got replaced during the mid-20th century by the use of thicker steel bars, now called rebars. Rebars then proved to provide greater strength and durability compared to mesh. But, this didn't end the era of mesh in construction applications.
In recent years, modern mesh reinforcement systems are back to play and are available in a variety of materials like steel, fiberglass, and synthetic materials. These systems provide customized designs based on the needs of the project.
There are mainly two types of mesh reinforcement used for concrete:1. Welded Wire Mesh
2. Expanded Metal Mesh
Types and Grades of Mesh Reinforcement
Mesh reinforcement can be made from various materials and the choice of the type depends on the application and design requirements. Here are some of the major types of mesh reinforcement based on material along with their standard codes and grades available. The data given below are based on American standards, ASTM and British Standards.1. Steel Mesh Reinforcement
This is the most common type of mesh reinforcement used in concrete construction. It is made from steel wires that are welded together to form a mesh pattern. Steel mesh reinforcement is available in various sizes and shapes, and can be made from different types of steel, including mild steel, high-tensile steel, and stainless steel. |
| Steel Mesh Reinforcement for Concrete Foundation |
The standard codes for steel mesh reinforcement and respective grades in ASTM and BS standards are mentioned in the table below.
|
STANDARD |
GRADE |
DETAILS |
|
ASTM A497/A497M |
Grade 40 [280
MPa] |
Standard
specification for steel welded wire reinforcement, deformed, for concrete |
|
Grade 60 [420
MPa] |
||
|
Grade 80 [550
MPa] |
||
|
ASTM A185/A185M |
Type I -
Welded wire fabric for general use |
Standard
specification for steel welded wire reinforcement, plain, for concrete |
|
Type II -
Welded wire fabric for marine use |
||
|
ASTM A1064/A1064M |
Grade 40 [280
MPa] |
Standard
specification for carbon-steel wire and welded wire reinforcement, plain and
deformed, for concrete |
|
Grade 60 [420
MPa] |
||
|
Grade 80 [550
MPa] |
||
|
BS4482 |
B500A - 500
MPa characteristic strength |
Specification
for steel wire for the reinforcement of concrete |
|
B500B - 500
MPa characteristic strength |
||
|
BS8666 |
A393 mesh -
10 mm wires at 200 mm centers |
Specification
for scheduling, dimensioning, bending and cutting of steel reinforcement for
concrete |
|
A252 mesh - 8
mm wires at 200 mm centers |
||
|
A193 mesh - 7
mm wires at 200 mm centers |
From the table above, it is clear that the grades vary based on whether the wires are welded, plain or deformed, or made from different steel types.
2. Fiberglass Mesh Reinforcement
 |
| Fiberglass Mesh Reinforcement for Wall Construction |
3. Synthetic Mesh Reinforcement
Synthetic mesh reinforcement is made from materials such as polypropylene, nylon, or polyester. It is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and has good tensile strength.Benefits of Mesh Reinforcement for Concrete
- Increased Strength: Mesh reinforcement provides increased strength to concrete structures by distributing loads and stresses evenly throughout the concrete. This helps to prevent cracking and other forms of structural failure.
- Improved Durability: Mesh reinforcement helps to improve the durability of concrete structures by preventing cracking due to thermal expansion and contraction, as well as other types of damage caused by environmental factors such as water, wind, and sun exposure.
- Cost-Effective: Mesh reinforcement is generally less expensive than other types of reinforcing steel. This makes it a cost-effective option for smaller projects or for applications where cost is a consideration.
- Ease of Use: Mesh reinforcement is easy to work with and shapes during the construction process. Its flexibility allows it to be easily molded into the desired shape without the need for specialized equipment.
- Corrosion Resistance: Mesh reinforcement is made from galvanized or epoxy-coated steel, which makes it less prone to corrosion than other types of reinforcing steel. This helps to ensure the long-term durability of the structure.
- Versatility: Mesh reinforcement can be used in a variety of concrete structures, including walls, floors, and foundations. Its flexibility and ease of use make it a versatile option for many different types of construction projects.
Mesh Reinforcement or Steel Rebars for Construction
When choosing between mesh reinforcement and steel reinforcement bars (rebar) for concrete, there are several factors that should be considered:|
FACTORS TO CONSIDER |
MESH REINFORCEMENT |
STEEL REINFORCEMENT BARS |
|
Load Requirements |
Suitable for
low to medium loads or stresses |
Suitable for
high loads or stresses |
|
Construction Site |
Easier to
handle and install in areas with limited space or difficult access |
More
challenging to handle and install in areas with limited space or difficult
access |
|
Budget |
Generally
less expensive than steel reinforcement bars |
Generally
more expensive than mesh reinforcement |
|
Design Requirements |
Suitable for
simple shapes and designs |
More
suitable for complex shapes and designs |
|
Corrosion Resistance |
Typically
coated for greater corrosion resistance |
May be more
appropriate for applications where greater corrosion resistance is needed |
De-Merits of Mesh Reinforcement
While mesh reinforcement has many benefits for reinforcing concrete structures, there are also some potential issues that should be considered:- Reduced Strength: Mesh reinforcement has a lower tensile strength than steel reinforcement bars, which means it may not be suitable for structures that will be subjected to high loads or stresses.
- Inadequate Placement: Mesh reinforcement can be susceptible to improper placement or installation, which can lead to weak spots in the concrete structure.
- Durability: While mesh reinforcement is typically coated to improve its resistance to corrosion, it may still be susceptible to rusting or other types of corrosion over time. This can lead to weakened concrete structures and reduced durability.
- Compatibility: Mesh reinforcement may not be compatible with certain concrete mixes, which can affect the overall strength and durability of the structure.
- Design Limitations: Mesh reinforcement may not be suitable for complex designs or shapes, as it is less flexible than steel reinforcement bars.
- Difficulty in Cutting: Mesh reinforcement can be difficult to cut and shape on-site, which can make it more challenging to work with than steel reinforcement bars.



0 Comments
Commenting Spam Links Are Against Policies