Search This Blog
Most Popular
What is a Transfer Beam?
May 27, 2020
Categories
- Building Construction (83)
- Building Materials (82)
- Columns (2)
- Concrete Beam (3)
- Concrete Construction Techniques (4)
- Concrete Mix Design (10)
- Concrete Repair (14)
- Concrete Slab (10)
- Construction Equipment (16)
- Construction News (7)
- Design of Structures (15)
- Engineering Drawing (1)
- Estimation (3)
- Geotechnical engineering (26)
- Highway Engineering (11)
- Innovations (30)
- Material Testing (9)
- Matrix Analysis of Structures (2)
- Mechanical Engineering (3)
- Strength of Materials (2)
- Structural Analysis (17)
- Structural Design (21)
- Structures (17)
- Transportation Engineering (9)
Plumbing Basics | Principle & Features
Neenu
February 01, 2023
Plumbing can be defined as a technology that designs, installs, and maintains pipes, fixtures, equipment, and accessories to convey fluids like water, gas, and wastewater within the building and around its premises.
To be more specific, plumbing is a skill required to transport water from the source to the treatment plants and take treated water to the users through a distribution system. While sanitary work refers to carrying wastewater to the waste disposal system (sewerage system) through plumbing fixtures.
A plumbing cycle refers to a mechanism through which the water is taken from the source, supplied to the user, and finally collected and treated wastewater is disposed of at the source. (Figure 2)
 |
Figure-2. Plumbing Cycle |
The building's plumbing system is crucial as it takes care of the hygiene requirements of the occupants. Hence, every plumbing system is properly planned and designed by a professional and experienced engineer or plumber. A plumber is a person engaged in plumbing activities and various related tasks.
This article explains the working principles, and fundamentals of plumbing systems for buildings and structures.
Working Principle of Plumbing System
Plumbing technology uses the basic principle law of nature - gravity, and pressure to move water as required.
The plumbing system of a building can be a system that brings fresh water into the building. This is called a domestic water system and it transports water under pressure. The system brings pressurized water into the structure for drinking, cooking, bathing, and other uses.
The second system takes wastewater from the building outwards to a sewer or septic system by means of gravity. It is called a sanitary waste system. Gravity pulls the waste along to the destination. To conduct this, the sewer plumbing lines are pitched or angled downward towards the sewer. It is also called a drain-waste-vent (DWV) plumbing system.
In addition to water transport plumb lines, there are natural-gas plumbing lines that deliver fuel to gas-burning cooktops, clothes dryers, furnaces, and water heaters.
Fundamentals of Plumbing System
Understanding the fundamentals of plumbing system helps to identify crucial plumbing problems in an existing building or to design a new system properly.
The domestic water system is a supply system that routes municipal water or groundwater (wells) to the building and branches out to several outlet fixtures like faucets, showers, toilets, bathtubs, and appliances like dishwashers, water heaters, and washing machines.
The drain-waste-vent system is a drainage system, where D is for the drain, to collect grey water [ the water from tubs, sinks, and washers], W is water from water closets [toilets & commodes], also called black water and V is for vent, for air movement.
The supply and drainage subsystems are two distinct operations that must not be overlapped.
A residential plumbing system is mainly composed of three main components:
- A water supply system that provides both hot and cold water to the fixtures.
- A fixture that delivers water
- A drain system (DWV)
The three components are given in the figure-2 below.
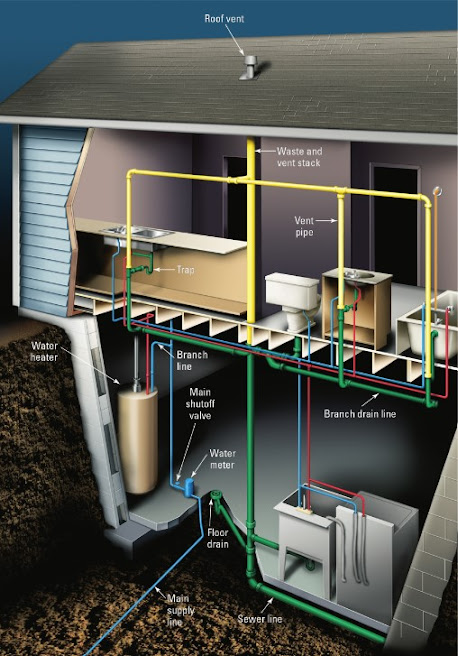 |
| Figure-1. Residential Plumbing System |
The domestic water supply to the building is taken by the blue plumb lines in Figure 2. Before supply to the building, there is a water meter to read the water supplied and a main shut off valve to shut the water supply services whenever necessary.
A branch line of main water supply is taken to the water heater, for hot water supply. This water line branches all fixture like washers, toilets, bath tubs, etc.
The red pumb lines in the Figure 2 are pipelines that take hot water from the water heater to the required fixtures.
The green plumb lines forms the drain lines for the movement of water away from the building. The DWV system consist of vents, traps and clean outs. These are important part of a DWV system to help the sewer move efficiently without any blockages or foul gases aways from the building.
 |
| Figure-2. DWV Plumbing System Image Credits: Plumbing Sniper |
As shown in the DWV system above, there are different types of vents and traps that is used based on the plumb line followed. The roof vents take air from the atmosphere to balance the whole air movement within the drain line and for easy movement of wastewater.
The sewer line can be connected finally to a septic system or to a municipal waste collection system.
The building plumbing system is complex and requires detailed evaluation and study. It is a combination of several plumbing fixtures, valves, drains, fittings, and components. A professional and experienced plumbing professional can only elicit a proper system of plumbing arrangement that works best for the plumb drawings provided by the engineer.
Read More On: What are Recirculating Hot Water Systems?
Most Visited
Sieve Analysis of Aggregates - ASTM Standard
August 11, 2021
How to Calculate Cement Required for Floor Tiling?
July 02, 2020
What are Infiltration Wells?
April 15, 2024
Cross-Section of a Road – Geometric Design of Highways
February 26, 2021
How to Choose Good Quality Aggregates for Construction?
August 10, 2021
Traverse Surveying - Objective, Method and Procedure
January 19, 2022
Construction ERP System – A Comprehensive Guide
December 12, 2024
Top 7 Waterproofing Materials for Concrete Roofs
December 13, 2024
Search This Blog
MUST READ
What is PERT? Objectives, Pros & Cons
September 10, 2017
Terzaghi's Equation: Soil Bearing Capacity for Foundations
March 02, 2022
Contact Form
Footer Menu Widget
Created By SoraTemplates | Distributed By Gooyaabi Templates


0 Comments
Commenting Spam Links Are Against Policies