Search This Blog
Most Popular
Categories
- Building Construction (87)
- Building Materials (85)
- Columns (2)
- Concrete Beam (3)
- Concrete Construction Techniques (6)
- Concrete Mix Design (15)
- Concrete Repair (14)
- Concrete Slab (11)
- Construction Equipment (17)
- Construction News (7)
- Design of Structures (19)
- Engineering Drawing (1)
- Estimation (3)
- Geotechnical engineering (26)
- Highway Engineering (11)
- Innovations (34)
- Material Testing (11)
- Matrix Analysis of Structures (2)
- Mechanical Engineering (3)
- Strength of Materials (2)
- Structural Analysis (13)
- Structural Design (24)
- Structures (17)
- Transportation Engineering (9)
4 Different Types of Geological Formations of Groundwater
Team Prodyogi
December 20, 2022
Groundwater occurs in many types of geological formations under the ground, some of which can be accessed from the surface, while some cannot.
 |
| Image Credits: Business Insider |
The major four types of water-bearing formations under the ground are:
- Aquifer
- Aquiclude
- Aquitard
- Aquifuge
1. Aquifer
An aquifer is a geological formation with groundwater within a permeable membrane that stores and allows transmission of water through it under ordinary field conditions. Unconsolidated sands and gravels are typical examples of aquifer formation. An aquifer is also called a water-bearing formation or groundwater reservoir .
 |
| Fig.2. Aquifer- Types |
An aquifer contains saturated material that yields significant quantities of water to wells and springs. Generally, an aquifer formation extends within a larger area and may overlie or be underlain by a confining bed or a relatively impervious material.
An aquifer can be an unconfined or confined aquifer. As aquifer is the major source of water compared; to aquiclude, aquitard and aquifuge; aquifer forms a major study of groundwater hydrology. When we dig a well penetrating a confined aquifer, we call it an artesian well, and a well penetrating an unconfined aquifer is called a water-table well. Read more on Groundwater Hydrology and Aquifers.
2. Aquitard
An aquitard is a geological formation with a poorly permeable membrane (semi-pervious) that permits the storage of water but is not capable of transmitting water in sufficient quantity. Sandy clay, shale, and silty clays (stratigraphic units) are examples of such formations.
An aquitard does not yield appreciable quantities of water to wells. As it is a semi-pervious nature, it transmits water at a slower rate compared to aquifers.
3. Aquiclude
Aquiclude is a geological formation of relatively impermeable material that permits the storage of water, but it is not capable of transmitting water in sufficient quantity. It does not yield appreciable quantities of water to wells. Clay is an example of such a formation.
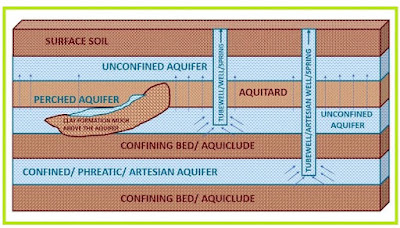 |
| Fig.4. Aquitard and Aquiclude |
4. Aquifuge
An aquifuge is a geological formation of relatively impermeable material that neither contains water nor transmits water. Solid granite belongs to this category of formation.
Also Read: Water Supply Engineering
Most Visited
Soil Sampling Methods| Undisturbed and Disturbed Samples
November 08, 2023
Boring Methods for Soil Exploration
November 02, 2023
What are Infiltration Wells?
April 15, 2024
Steel Column Connected to Concrete Masonry Wall
October 11, 2017
How to Choose Good Quality Aggregates for Construction?
August 10, 2021
Terzaghi's Equation: Soil Bearing Capacity for Foundations
March 02, 2022
Structure of Timber |Macrostructure and Microstructure
March 22, 2024
Search This Blog
MUST READ
What is PERT? Objectives, Pros & Cons
September 10, 2017
Terzaghi's Equation: Soil Bearing Capacity for Foundations
March 02, 2022
Contact Form
Footer Menu Widget
Created By SoraTemplates | Distributed By Gooyaabi Templates


0 Comments
Commenting Spam Links Are Against Policies