Search This Blog
Most Popular
Categories
- Building Construction (83)
- Building Materials (82)
- Columns (2)
- Concrete Beam (3)
- Concrete Construction Techniques (4)
- Concrete Mix Design (9)
- Concrete Repair (14)
- Concrete Slab (10)
- Construction Equipment (16)
- Construction News (7)
- Design of Structures (15)
- Engineering Drawing (1)
- Estimation (3)
- Geotechnical engineering (26)
- Highway Engineering (11)
- Innovations (30)
- Material Testing (10)
- Matrix Analysis of Structures (2)
- Mechanical Engineering (3)
- Strength of Materials (2)
- Structural Analysis (17)
- Structural Design (21)
- Structures (17)
- Transportation Engineering (9)
Sheet Piles
Sheet piles are pile walls constructed to provide temporary/permanent ground support during deep excavations and basement construction. Sheet piles are sections of sheet materials with interlocking edges. Sheet piling is the process of driving or pushing these sheet piles into the ground. The sheet piles are usually thin in cross-section and low-weight.
 |
| Image Courtesy: http://www.constructionbuilding.net/ |
Working of Sheet Piles
Each sheet pile driven into the soil interlocks with each other to form a strong connecting structure. The sheet piling is performed in a sequence along the planned excavation perimeter of the project.
The whole arrangement of sheet piles provides earth support and give additional lateral support by providing anchors.
The sheet piles are designed narrow, and the strength and stability of the pile wall are defined by the shape and material of the sheet. Among the different materials used, steel sheet piles are the most appropriate material for withstanding bending forces and pressure.
Sheet piles can be installed into the soil by:
- Vibration: This is the common method of driving sheet piles into the soil, using a vibratory hammer. After installing the first pile, a second pile is hammered to interlock with the first by vibration.
- Pressing: The sheet piles are pressed into the ground using the hydraulic machine. This is used when noise and vibration issues are a concern. It is a time-consuming process.
- Excavation: Long trench is excavated and filled with bentonite to prevent the sidewall collapse. Followed by installing sheet piles in the trench. The cement bentonite slurry is then allowed to set.
Materials Used for Sheet Piles
Sheet piles can be made of timber, concrete, and steel.
1. Timber Sheet Piles
Timber sheet piles or wakefield piles are traditional sheet piling material that follows an interlocking system based on the tongue and groove concept. The method serves to keep the wall aligned while providing a longer path against infiltration with more potential contact points than a simple butt joint. It is extensively used in retainment work for shallow trenches and land cofferdams, where water intrusion is not a concern.
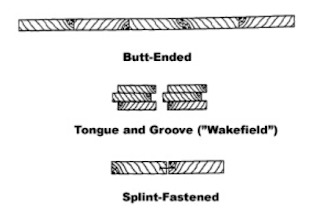 |
Timber Sheet Pile Interlock Connection System |
The main disadvantage of timber sheet piles is that they require preservative treatment and not suitable for soils with stones.
2. Reinforced Concrete Sheet Piles
R.C.C sheet piles are formed by making precast concrete sheet piles members. These too are connected using the tongue and groove joints. They are usually 6 to 12 inches deep and 30 to 48 inches wide.
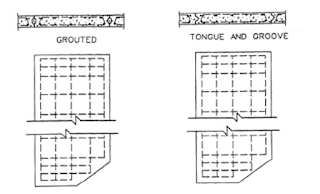 |
| Concrete Sheet Piles |
Concrete sheet piles are usually prestressed to facilitate handling and driving. They are manufactured with special corner and angles sections. In a grouted type joint, the joint is cleaned and it is grouted only after driving the pile into suitable depth.
Concrete sheet piles are used for marine environments, streambeds with high abrasion, and axial load action.
3. Steel Sheet Piles
|
Normal Sections |
Straight Web Sections |
Box Sections |
Composite Sections |
|
1. Larssen Sheet Piles (U-Section) 2. Frodingham Sheet Piles (Z-Section) |
Straight web sheet piles are designed to form cylindrical structures
, generally closed. |
Here two or more sheet pile sections are welded together to form a
pile wall. |
Combination of one or more profile of sheet piles. |
|
Good driving qualities, good strength, and low weight. Effective
interlocking and sealing. |
They are used to construct piles that are liable to be subjected to
tensile forces. |
Used to resist heavy loads and high bending moments. |
Used in water front protection. |
|
Larssen sheet piles are strong and easier to penetrate into the
ground due to their uniform shape. |
They are used in the cellular cell structures like cofferdams and
diaphragm cell structures. |
|
|
|
Fordingham sheet piles are supplied as interlocked pai. It is easier
to handle and pitch. |
|
|
|
4. Light-Gauge Aluminum Sheet Piles
Aluminum sheet piles are interlocking corrugated sheet piles made from aluminum alloy 5052 or 6061. These sheet pile sections have relatively low-section modulus and moment of inertia.
5. Vinyl Sheet Piling
A new type of sheet pile material is prominently used for sea walls and other applications. The raw material is a plastic resin and comes in different configurations, mainly Z. Each sheet pile has interlocking male and female edges.
It is best suited for marine environments and is not subjected to leaching, corrosion, or similar deteriorations like steel. These sheet piles possess a low modulus of elasticity and strength compared to sheet piles.
6. Pultruded Fiberglass Sheet Piling
Pultruded sheet piling is a section of piling that is manufactured by the continuous processing of raw materials by pulling resin-rich reinforcements through a heated steel die to form profiles of a constant cross-section of continuous length. It is used for light bulkheads.Among the materials mentioned, pultruded sheet piles and vinyl sheet piles must be designed to resist higher deflection.
Selection of Sheet Piles
- The type of construction work -temporary/permanent
- The site conditions
- The water table level
- The required depth of piles
- The bending moments involved
- The type of soil
- The nature of the structure
- The type of protection required
Advantages of Sheet Piles
- Sheet piles are lightweight, easily transported, and handled
- It is recyclable and reusable.
- The pile length and design is easily adapted
- Joints can be designed to withstand high pressure
- Low maintenance underwater
Disadvantages of Sheet Piles
- If the soil is rocky or has large boulders, the installation is difficult
- High vibration and noise to surrounding, if vibration method of installation is performed
- Removal of temporary sheet piles is costly





0 Comments
Commenting Spam Links Are Against Policies