Search This Blog
Most Popular
Understanding Construction Project Phases
Sieve Analysis of Aggregates - ASTM Standard
Categories
- Building Construction (83)
- Building Materials (82)
- Columns (2)
- Concrete Beam (3)
- Concrete Construction Techniques (4)
- Concrete Mix Design (9)
- Concrete Repair (14)
- Concrete Slab (10)
- Construction Equipment (16)
- Construction News (7)
- Design of Structures (15)
- Engineering Drawing (1)
- Estimation (3)
- Geotechnical engineering (26)
- Highway Engineering (11)
- Innovations (30)
- Material Testing (9)
- Matrix Analysis of Structures (2)
- Mechanical Engineering (3)
- Strength of Materials (2)
- Structural Analysis (17)
- Structural Design (21)
- Structures (17)
- Transportation Engineering (9)
Drone Mapping| Aerial Mapping Methods in Construction
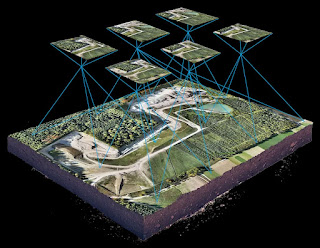
Drone mapping is the practice of acquiring hundreds of aerial images using drones and stitching them together digitally with specialized mapping software to develop a larger and more accurate composite image. The surveying principle used for drone mapping is photogrammetry.
Photogrammetry is the science of making measurements from photographs. A drone of a UAV flies over the predetermined subject property to capture hundreds of photos in a straight down and oblique direction to finally create a digital representation of reality and collect data from it.
Drone Mapping with GPS
Standard drone mapping without the use of GPS is simply a vehicle with a camera. There is no particular setting employed to position it in the sky and is not accurately geotagged. Drone hardware alone cannot provide the relational position data.
Ground Control Points (GCPs) for Drone Mapping
A solution for this is the use of Ground Control Points (GCPs). GCPs are known points ( x, y, z coordinates data) that are marked and measured on the ground using a base, rover, and GPS or by using Aeropoints. The base is a fixed receiver and the rover is a moving receiver. GCPs greatly increase the global accuracy of drone maps. GCPs are not necessary for all drone mapping projects. But they are a vital tool for precision mapping.
 |
| Drone Mapping using Ground Control Points (GCPs) |
As shown in the figure above, a ground control point is already known with coordinates (450,000,3500000, 180). The drone mapping takes drone images, which include this GCP which helps in accurate imaging and photogrammetric analysis.
💡Note
AeroPoint is a portable, reusable ground control point (GCP) that repeatedly records positioning data while you fly. Lightweight and durable with simple one-touch operation, a standard set of 10 AeroPoints can be placed around a survey area in minutes.
Some of the features of ground control points in drone mapping are:
- The GCPs selected for drone mapping must be evenly distributed throughout the area under survey.
- A minimum of three GCPs is always recommended. The number of GCPs is dependent on the size of the survey area.
- GCPs must be located on the ground such that it is easily identifiable and visible in the drone mapping images. These points can be either made or bought. The basic requirements of GCPs are a Minimum size of 0.5 m x 0.5m, Highly contrasting, and the center point must be easily identified.
- If the survey has noticeable elevation changes, the GCPs must be placed on the highest as well as lowest points.
- Make sure the GCPs provided are clearly seen from the air and not covered by vegetative and any other obstructions like trees, buildings, etc.


0 Comments
Commenting Spam Links Are Against Policies