Search This Blog
Most Popular
Sieve Analysis of Aggregates - ASTM Standard
August 11, 2021
Categories
- Building Construction (83)
- Building Materials (82)
- Columns (2)
- Concrete Beam (3)
- Concrete Construction Techniques (4)
- Concrete Mix Design (9)
- Concrete Repair (14)
- Concrete Slab (10)
- Construction Equipment (16)
- Construction News (7)
- Design of Structures (15)
- Engineering Drawing (1)
- Estimation (3)
- Geotechnical engineering (26)
- Highway Engineering (11)
- Innovations (30)
- Material Testing (9)
- Matrix Analysis of Structures (2)
- Mechanical Engineering (3)
- Strength of Materials (2)
- Structural Analysis (17)
- Structural Design (21)
- Structures (17)
- Transportation Engineering (9)
Types of Bridge Bearings Used in Construction- As Per AASHTO
Neenu
January 04, 2022
Bridge bearings are structural devices placed between the superstructure and substructure of a bridge. As per AASHTO (American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials).
Usually, they are classified into:
- Fixed bearings
- Expansion bearings
Read More On: What are Bridge Bearings?
 |
| Types of Bridge Bearings Used in Construction |
Fixed Bearings
Fixed bearings are bearings that allow rotations but restrict translational movements.
Expansion Bearings
Expansion bearings allow both rotational and translational movements.
Types of Bridge Bearings
The principal type of bearings used in bridges are:
- Sliding bearings
- Rocker and pin bearings
- Roller bearings
- Elastomeric bearings
- Curved bearings
- Pot bearings
- Disk bearings
1. Sliding Bearings
- Sliding bearing is a bearing type that utilizes one plane metal plate sliding against another to accommodate translations.
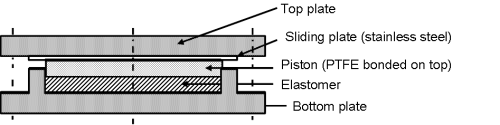 |
| Sliding Bearings |
- The sliding bearing surface produce a frictional force that is applied to the superstructure, the substructure, and the bearing itself. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is usually applied on one of the plate to reduce the friction. Hence, a PTFE coated steel plate slides over a stainless steel plate. ( As per AASHTO Standards).
- Sliding bearings are limited to span length of 15 m or less ( AASHTO)
- Sliding bearings alone are used when the rotations caused by the supports are negligible. In other cases, they are used in combination with other bearing types.
- In the above figure, sliding plate is used in combination with elastomer.
2. Rocker and Pin Bearings
 |
| Fig.2. (a) Rocker Bearing (b) Pin Bearing (c) Roller Bearing |
A rocker bearing is a type of expansion bearing. As shown in the fig-2(a), it consists of pin at the top that permits rotations and a curved surface at the bottom that permits translational movement.
The upper plate is connected to the sole plate and the lower plate sits on the masonry plate. Keys are used to keep the rocker in place and prevent walking.
Pin bearing is a type of fixed bearing that accommodates rotations through the use of steel pin. It has a similar configuration compared with rocker bearing, except that the bottom curved rocker plate is flat and anchored directly to the concrete pier. ( Fig.2b)
Rocker and pin bearings are primarily used in steel bridges. It is applied where the direction of displacement is well-defined, as they permits translations and or rotations in one direction.
They can support heavy loads with adequate vertical clearance provided.
3. Roller Bearings
Roller bearings consist of one or more rollers between two parallel steel plates, fig.2(c). Single roller bearings facilitate both translational and rotations in longitudinal direction. A group of rollers accommodate only translational in longitudinal direction. Here, rotations are provided by combining rollers with a pin bearing.
Roller bearings can be used for both steel and concrete bridges. Single rollers are cheap but take limited vertical loads. Multiple roller bearings supports very large loads but are very expensive.
4. Elastomeric Bearings
Elastomeric bearings are bearings made out of natural or synthetic rubber elastomers. These bearings accommodates both translational and rotational movement through the deformation of the elastomer.
Elastomer is flexible in shear but are act very stiff towards volumetric changes. When compressive load is applied to the elastomers, they expand laterally. To sustain large load and related excessive deflection, reinforcement is used to restrain lateral bulging of the elastomer.
Hence, there comes several types of elastomeric bearing pads to meet this requirement.
5. Curved Bearings
Curved bearings consist of two matching curved plates with one sliding against the other to accommodate rotations. The curved surfaces used can be either cylindrical which allows the rotations about one axis or spherical which allows the bearing to rotate about any axis.
Pot bearings consist of a plain elastomeric disk confined in a shallow ring or a pot as shown in the fig.5 below. Steel piston that is closely fitted to the steel ring is used to transmit the vertical loads. The elastomeric pads are confined within the flat sealing rings. The elastomers act like a viscous fluid when the bearing rotates. As these elastomers are confined, they can take up heavy vertical loads than conventional elastomeric pads.
Pure pot bearing restrains translational movement and lateral loads are transferred through the steel piston. A PTFE sliding surface is used to accommodate translational movement.
7. Disk Bearing
A disk bearing utilizes a hard elastomeric disk to support the vertical loads and a metal key in the center of the bearing to resist the horizontal loads.
The deformation of the elastomers accommodates, rotational movement. A PTFE slider is used to accommodate the translational movement.
Most Visited
Sieve Analysis of Aggregates - ASTM Standard
August 11, 2021
How to Calculate Cement Required for Floor Tiling?
July 02, 2020
What are Infiltration Wells?
April 15, 2024
Cross-Section of a Road – Geometric Design of Highways
February 26, 2021
How to Choose Good Quality Aggregates for Construction?
August 10, 2021
Traverse Surveying - Objective, Method and Procedure
January 19, 2022
Construction ERP System – A Comprehensive Guide
December 12, 2024
Top 7 Waterproofing Materials for Concrete Roofs
December 13, 2024
Search This Blog
MUST READ
What is PERT? Objectives, Pros & Cons
September 10, 2017
Terzaghi's Equation: Soil Bearing Capacity for Foundations
March 02, 2022
Contact Form
Footer Menu Widget
Created By SoraTemplates | Distributed By Gooyaabi Templates





0 Comments
Commenting Spam Links Are Against Policies