Search This Blog
Most Popular
Sieve Analysis of Aggregates - ASTM Standard
August 11, 2021
Rainwater Harvesting in Buildings
November 01, 2024
Categories
- Building Construction (77)
- Building Materials (75)
- Columns (2)
- Concrete Beam (3)
- Concrete Construction Techniques (4)
- Concrete Mix Design (9)
- Concrete Repair (12)
- Concrete Slab (10)
- Construction Equipment (15)
- Construction News (7)
- Design of Structures (15)
- Engineering Drawing (1)
- Estimation (3)
- Geotechnical engineering (25)
- Highway Engineering (11)
- Innovations (27)
- Material Testing (8)
- Matrix Analysis of Structures (2)
- Mechanical Engineering (3)
- Transportation Engineering (9)
Breaking Down Project Management: Guide to Types of Breakdown Structures
Neenu
March 16, 2023
A breakdown structure in project management refers to a hierarchical structure that breaks down a project's scope and deliverables into smaller, more manageable components. It is a graphical representation that illustrates the relationship between the components of the project, and how they fit together to achieve the project's objectives.
The idea of breaking down a task or service into a series of individual processes and studying the relationship between these processes is the theory behind scientific management. It is known as tree diagrams required to visualize parent-to-child relationships in a complete task.
In 1911 Frederick Taylor, the Father of Scientific Management published the Principles of Scientific Management which proposes work methods and management strategies to increase worker productivity. These scientific management principles are the start of many modern project management processes that are built around "breakdown structures". Breakdown structures are used in project management as a tool in various fields of projects.
The various types of breakdown structures for project management are Work Break Down Structure (WBS), Product Breakdown Structure (PBS), Resource Breakdown Structure (RBS), and Organization Breakdown Structure (OBS).
 |
1. Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
The Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) breaks down the project into smaller work components, called work packages, which are more manageable and easier to estimate schedule and assign to team members. The WBS is often presented in a tree-like structure, with the main project objective at the top, and progressively smaller work packages branching off from it. It is a basic step followed for various network analyses like PERT and CPM.Here is an example of a work breakdown structure (WBS) for a construction project:
This is just an example, and the specifics of a WBS for a construction project will depend on its size, scope, and complexity. The WBS should be customized to fit the needs of each specific project, and it should be reviewed and updated regularly throughout the project lifecycle.
The RBS typically includes three levels of detail: the top level is the main resource category, such as labor or materials, the second level breaks down each resource category into subcategories, and the third level provides further details about each subcategory.
Here is an example of a Resource Breakdown Structure for a construction project:
Here is an example of a Product Breakdown Structure for a construction project:
The PBS provides a comprehensive overview of the final product, allowing project managers to better understand the project's scope and deliverables. It can also help to identify any potential design or construction issues that may arise during the project and address them proactively. The PBS can be used to estimate costs, allocate resources, and track progress against project milestones.
The OBS can help project managers better understand the organizational structure of the construction company or project team, and ensure that everyone is working together effectively to achieve the project's objectives. It can also help to identify any potential communication or resource allocation issues that may arise during the project and address them proactively.
1. Project Initiation
- Conduct site survey and analysis
- Obtain necessary permits and licenses
- Develop project charter
- Develop architectural plans and engineering designs
- Create a detailed project schedule and budget
- Obtain necessary approvals from regulatory bodies
- Clear the site and demolish any existing structures
- Excavate the site and prepare the foundation
- Install utilities such as water, electricity, and sewage
4. Construction
- Frame and erect building structure
- Install roofing and exterior cladding
- Install plumbing, electrical, and HVAC systems
5. Interior Finishing
- Install drywall and paint interior walls
- Install flooring and finish carpentry
- Install fixtures and appliances
6. Testing and Commissioning
- Test systems and equipment for functionality and safety
- Conduct building inspections and obtain necessary certifications
- Commission the building for occupancy
7. Project Closeout
- Conduct a final walk-through and punch list
- Obtain final approvals and permits
- Close out contracts and finalize project budget
This is just an example, and the specifics of a WBS for a construction project will depend on its size, scope, and complexity. The WBS should be customized to fit the needs of each specific project, and it should be reviewed and updated regularly throughout the project lifecycle.
2. Resource Breakdown Structure (RBS)
The Resource Breakdown Structure (RBS) is a hierarchical chart that breaks down a construction project's resources into smaller, more manageable categories. It is similar to the Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) in that it breaks down a project into smaller components, but instead of breaking down the work, it breaks down the resources needed to complete the work. The RBS is often used in conjunction with the WBS to ensure that all required resources have been identified, estimated, and allocated.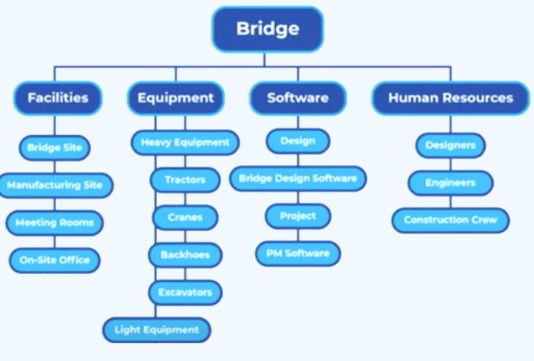 |
| Image Credits: Teamly |
The RBS typically includes three levels of detail: the top level is the main resource category, such as labor or materials, the second level breaks down each resource category into subcategories, and the third level provides further details about each subcategory.
Here is an example of a Resource Breakdown Structure for a construction project:
1. Labor
- Project Manager
- Site Supervisor
- Skilled Labor
- Unskilled Labor
2. Materials
- Concrete
- Steel
- Wood
- Glass
3. Equipment
- Cranes
- Excavators
- Concrete Mixers
- Scaffolding
3. Product Breakdown Structure (PBS)
In construction management, a Product Breakdown Structure (PBS) is a hierarchical chart that breaks down the project's final product or deliverables into smaller, more manageable components. The PBS provides a detailed description of the features and characteristics of the final product and identifies the key components required to create the product.
The PBS is often used in conjunction with the Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) and Resource Breakdown Structure (RBS) to ensure that each component of the final product is aligned with the project's objectives and that resources are allocated effectively and efficiently.
The PBS is often used in conjunction with the Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) and Resource Breakdown Structure (RBS) to ensure that each component of the final product is aligned with the project's objectives and that resources are allocated effectively and efficiently.
1. Building Envelope
- Foundation
- Exterior Walls
- Roof
- Windows and Doors
- InteriorWalls and Partitions
- Flooring
- Ceiling
- Doors and Hardware
2. Mechanical and Electrical Systems
- Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC)
- Electrical Systems
- Plumbing Systems
- Fire Protection Systems
3. Site Work
- Site Preparation
- Grading and Drainage
- Paving and Sidewalks
- Landscaping
The PBS provides a comprehensive overview of the final product, allowing project managers to better understand the project's scope and deliverables. It can also help to identify any potential design or construction issues that may arise during the project and address them proactively. The PBS can be used to estimate costs, allocate resources, and track progress against project milestones.
4. Organization Breakdown Structure (OBS)
The Organization Breakdown Structure (OBS) in construction is a hierarchical chart that shows the organizational structure of a construction company or project team. The OBS breaks down the organization into smaller, more manageable components, such as departments or work teams, and assigns specific responsibilities and roles to each component or member.
Here is an example of an Organization Breakdown Structure for a construction project:
Here is an example of an Organization Breakdown Structure for a construction project:
1. Company
- Project Manager
- Finance Department
- Human Resources Department
- Marketing Department
2. Project Team
- Site Supervisor
- Construction Crew
- Design Team
- Quality Control Team
3. Subcontractors
- Excavation Contractor
- Concrete Contractor
- Electrical Contractor
- Plumbing Contractor
Is Breakdown Structure Necessary for Project Management?
Breakdown structure has been paramount for project management since the industrial revolution era. The breakdown structures in construction play a crucial role in project planning, management, and control. Here are some reasons why the breakdown structure is important in construction:
- Defines the scope of the project: The breakdown structure helps to define the project's scope by breaking down the project into smaller, more manageable components. This makes it easier to understand the project's objectives, deliverables, and requirements.
- Facilitates project planning: The breakdown structure provides a framework for project planning, allowing project managers to identify the resources needed, estimate costs, and develop a project schedule. It also helps to identify potential risks and develop strategies to mitigate them.
- Helps with resource allocation: The Resource Breakdown Structure (RBS) helps to identify the resources required for each component of the project, making it easier to allocate resources effectively and efficiently.
- Improves communication: The breakdown structure provides a common language and understanding of the project among team members, stakeholders, and clients. It helps to improve communication and collaboration, reducing the risk of misunderstandings and errors.
- Enables progress tracking: The breakdown structure provides a basis for tracking progress against the project plan. This makes it easier to monitor project performance, identify deviations from the plan, and take corrective actions when necessary.
- Enhances project control: The breakdown structure helps to establish a framework for project control, allowing project managers to monitor and control the project's progress, costs, and risks.
Read More On: Types of Work Breakdown Structures (WBS) in Construction
Most Visited
Terzaghi's Equation: Soil Bearing Capacity for Foundations
March 02, 2022
Traverse Surveying - Objective, Method and Procedure
January 19, 2022
Structure of Timber |Macrostructure and Microstructure
March 22, 2024
What are Infiltration Wells?
April 15, 2024
How to Calculate Cement Required for Floor Tiling?
July 02, 2020
What is Target Mean Strength? R.C.C Design
July 17, 2021
Sieve Analysis of Aggregates - ASTM Standard
August 11, 2021
Search This Blog
MUST READ
What is PERT? Objectives, Pros & Cons
September 10, 2017
Terzaghi's Equation: Soil Bearing Capacity for Foundations
March 02, 2022
Contact Form
Footer Menu Widget
Created By SoraTemplates | Distributed By Gooyaabi Templates



0 Comments
Commenting Spam Links Are Against Policies